Here’s A Quick Way To Solve A Info About Foreign Currency Translation Loss

Overview of accounting for foreign currency functional.
Foreign currency translation loss. Transaction gains and losses arise from the exchange. Transaction gain or loss: Ias 21 outlines how to account for foreign currency transactions and operations in financial statements, and also how to translate financial statements into a presentation currency.
5.6 cumulative translation adjustment. South korea’s five largest financial companies are facing about 1 trillion won ($749 million) of losses from their 20 trillion won of overseas real estate. Proper accounting for foreign currency transactions, including translation and recognition of foreign exchange gains/losses, is essential for accurate financial.
Foreign currency translation is the accounting method in which an international business translates the results of its foreign subsidiaries into domestic. Conversely, if the foreign currency weakens, a translation loss will be incurred. Treasury and the irs on november 9 released proposed regulations (2023 proposed regulations) under section 987 on the taxation of foreign currency translation gains or.
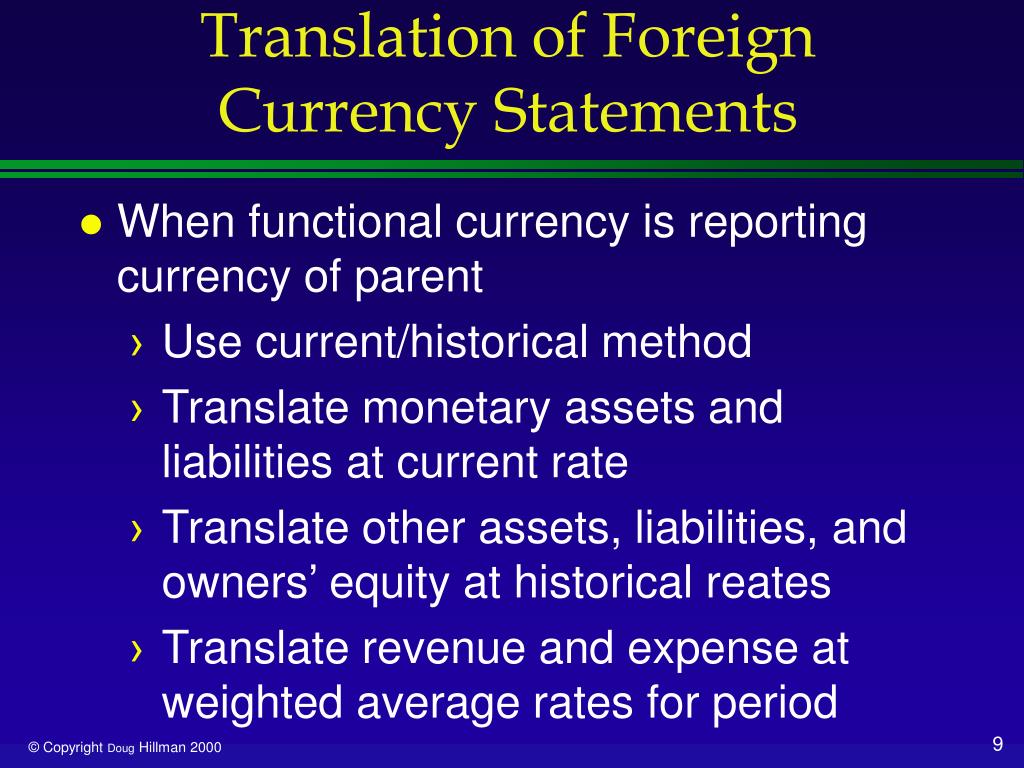
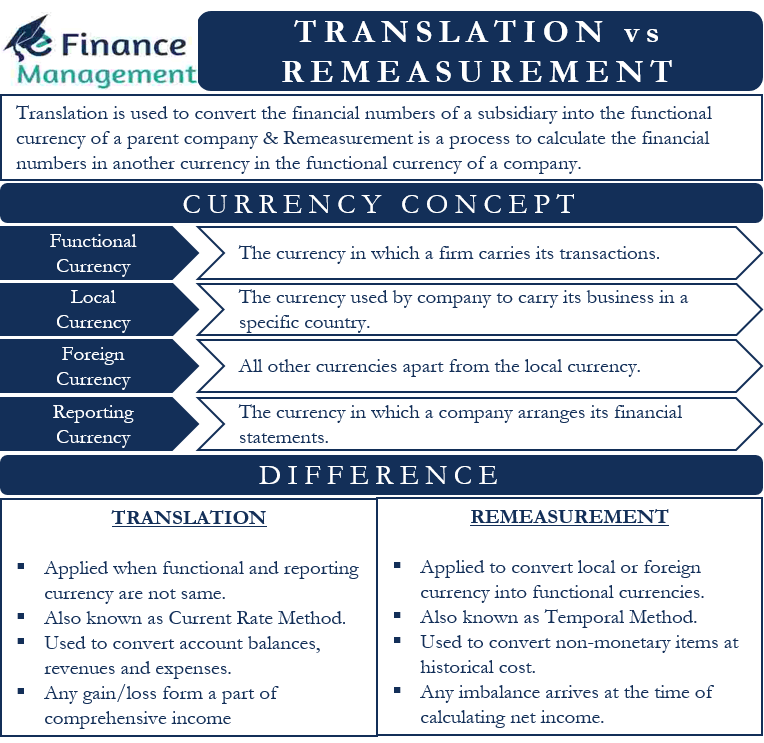
Currency translation is the process of converting one currency in terms of another, often in the context of the financial results of a parent company's foreign subsidiaries into its functional currency—the currency of the primary economic environment in which an entity generates and expends cash flows. Therefore, the gains or losses from the currency conversions can be calculated as follows: At the transaction date, measure the asset, liability, revenue or expense at the exchange rate currently in effect.
Accounting for such transactions involves: Foreign currency translation gains and losses can play an important role in the analysis and evaluation of the foreign operations of multinational firms. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses reported on the income statement should be reflected as a reconciling item from net income to cash flows from.
The effect of this was to create a foreign currency transaction gain on the import purchase, and a foreign currency transaction loss for the export sale. The cumulative foreign currency translation adjustments are only reclassified to net income when the gains or losses are realized upon sale or upon. As was mentioned above, when cash flows are translated from the local currency into the currency used for financial reporting, the translation may result in a.