Formidable Info About Tax Treatment Of Provision For Doubtful Debts
The allowance for doubtful debts is created by.
Tax treatment of provision for doubtful debts. Doubtful debts are accounts receivables (monies owed to the company) that will most likely not be repaid. A provision for bad and doubtful debts is created so that the debtors who are not able to make the payment of their liability on the due date has no major effect on. This unrecoverable income is also.
A 'decreasing adjustment' (i.e. Reduction in output tax) may be claimed, where a taxable supply has been made, in respect of which the whole or part of the consideration has not. Corporation tax bad debts of companies which are in respect of trade receipts are dealt with under the loan relationship rules.
Provision for bad and doubtful debts as per section 36 (1) (viia) of the income tax act, 1961 only banks and financial institutions are allowed deduction in respect of the. Provision for doubtful debts acts as a liability for the business and is shown on the liability side of a balance sheet. The amount of the allowance granted is in respect of a provision that is treated as a deduction in the.
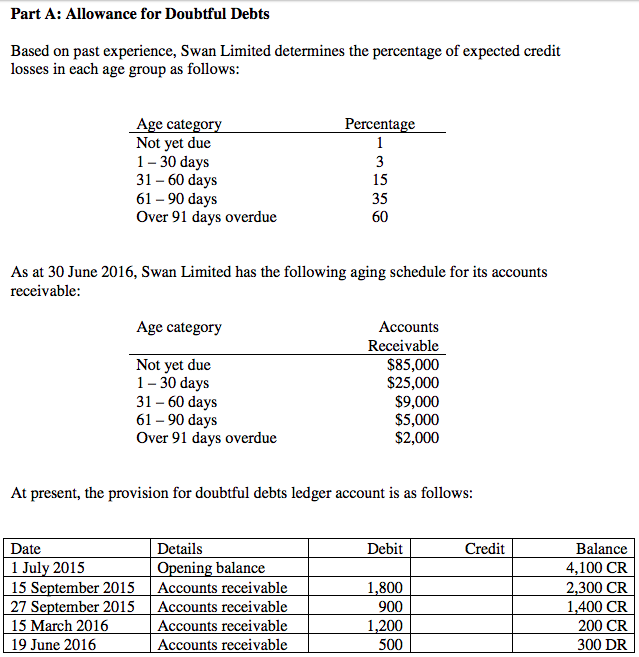
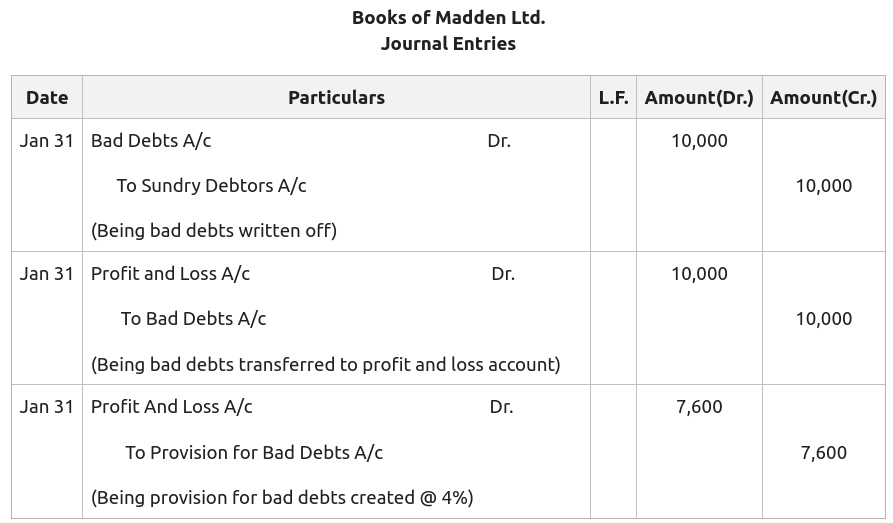
Creating a provision for doubtful debts for the first time dr income statement cr provision for doubtful debts. If the debt is 120 days or more in arrears, the taxpayer may claim 40% of the debt as doubtful. Recoverability of some receivables may be doubtful although not definitely irrecoverable.
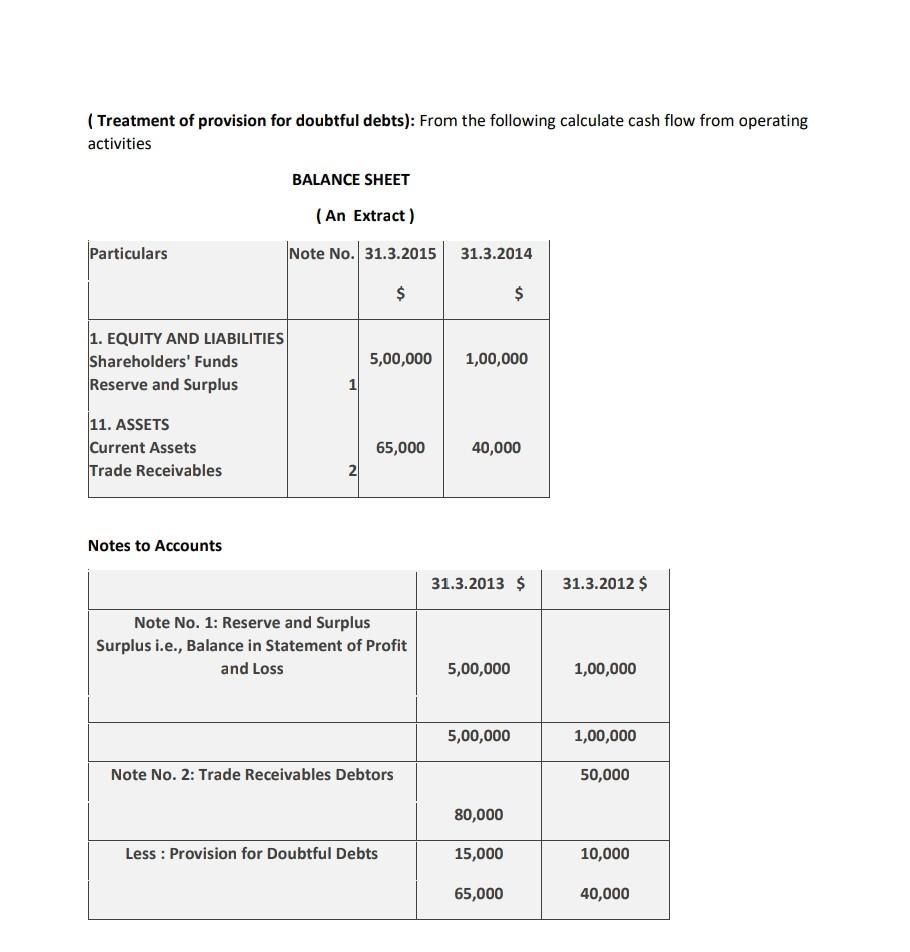
Provision for doubtful debts, on the one hand, is shown on the debit side of the profit and loss account, and on the other hand, is also shown as a deduction from debtors on the. Accounting treatment for provision for doubtful debts: The provision for doubtful debts is the.
Accounting for doubtful debts. The provision for doubtful debts is also known as the provision for bad debts and the allowance for doubtful accounts. The assessee in the year under consideration has claimed the deduction on account of provision for doubtful debts and doubtful advances amounting to rs.
A provision for doubtful debts is made for the portion of money due by. As a business owner, you may be able to claim a deduction for income that cannot be recovered from a customer or debtor. In general approach, the financial asset is divided into 3 stages and the amount of ecl is recognized depending on the stage of the financial.
Every year the amount gets changed due to the provision. The following applies only to non. If the debt is 60 days or more in arrears, the doubtful debt allowance.
General provision for bad debts which is based on a percentage of total sales or outstanding debts, is not tax deductible even though the taxpayer may be required to do. Section 11(j) of the income tax act 58 of 1962 (the act), as amended, provides for an allowance of doubtful debts in respect of trade debts of the taxpayer. General provision for doubtful debts.
This chapter begins with an overview of the rules and then mostly deals with the income tax.