Neat Info About Deferred Tax Liabilities In Balance Sheet
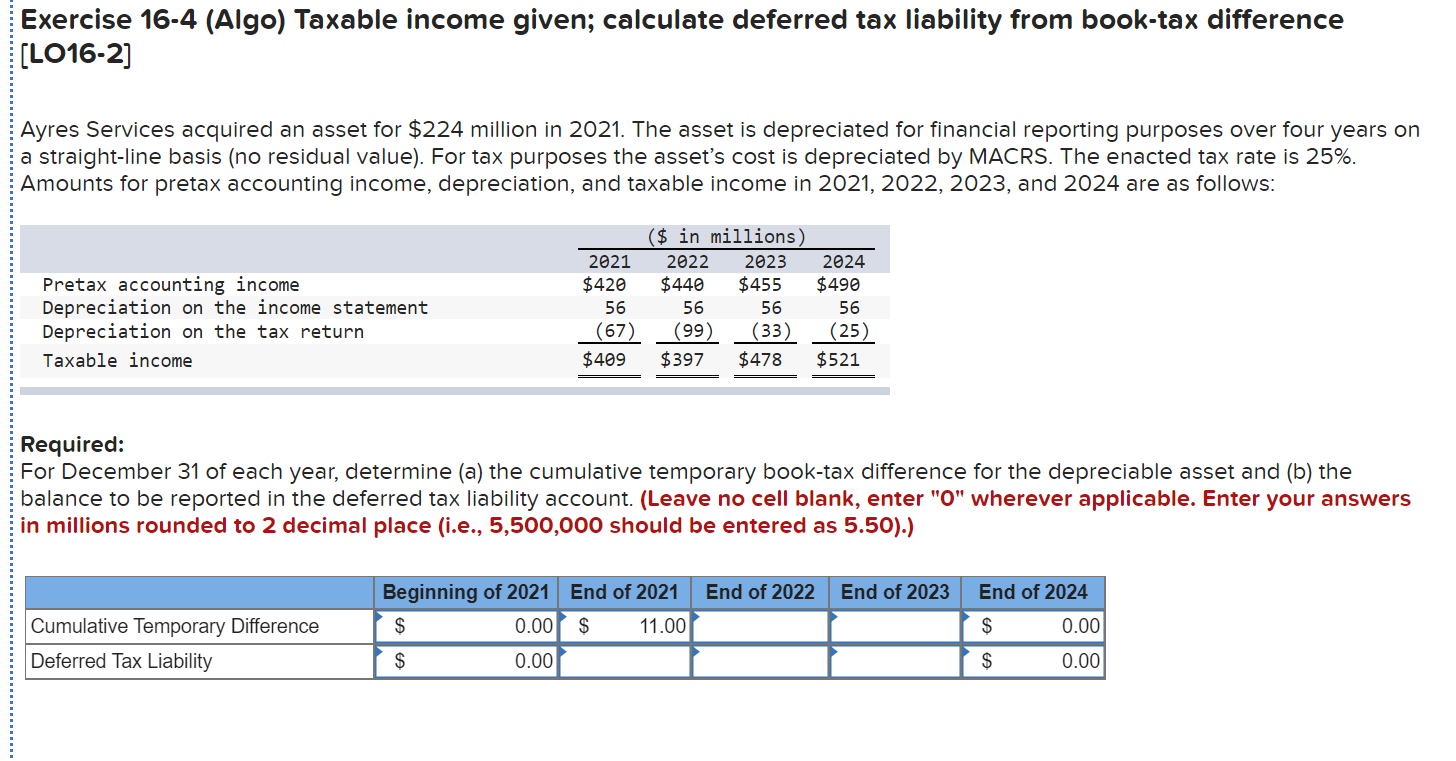
For example, if tax rules allow faster depreciation than accounting rules, taxable profits will be lower than accounting profits in early years, but the opposite happens later.
Deferred tax liabilities in balance sheet. Depreciation on plants, properties and equipment 2. Deferred tax liability is a liability that is due in the future. It is the opposite of a deferred tax liability, which represents.
So, in simple terms, deferred tax is tax that is payable in the future. Deferred tax assets and liability should be netted off, meaning that only. It is important to note that deferred taxes can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements.
Following are the general circumstances, that can be found easily in financials of any company: Deferred tax liability is a tax credit for the business that will need to be paid in the future, while a deferred tax asset is a tax credit for current or future taxes. A deferred tax asset is a business tax credit for future taxes, and a deferred tax liability means the business has a tax debt that will need to be paid in the future.
Deferred tax liability (dtl) or deferred tax asset (dta) forms an important part of financial statements. Frs 102 paragraph 29.24a requires deferred tax assets and liabilities to be. Deferred tax liabilities (dtl) and assets (dta) are opposites.
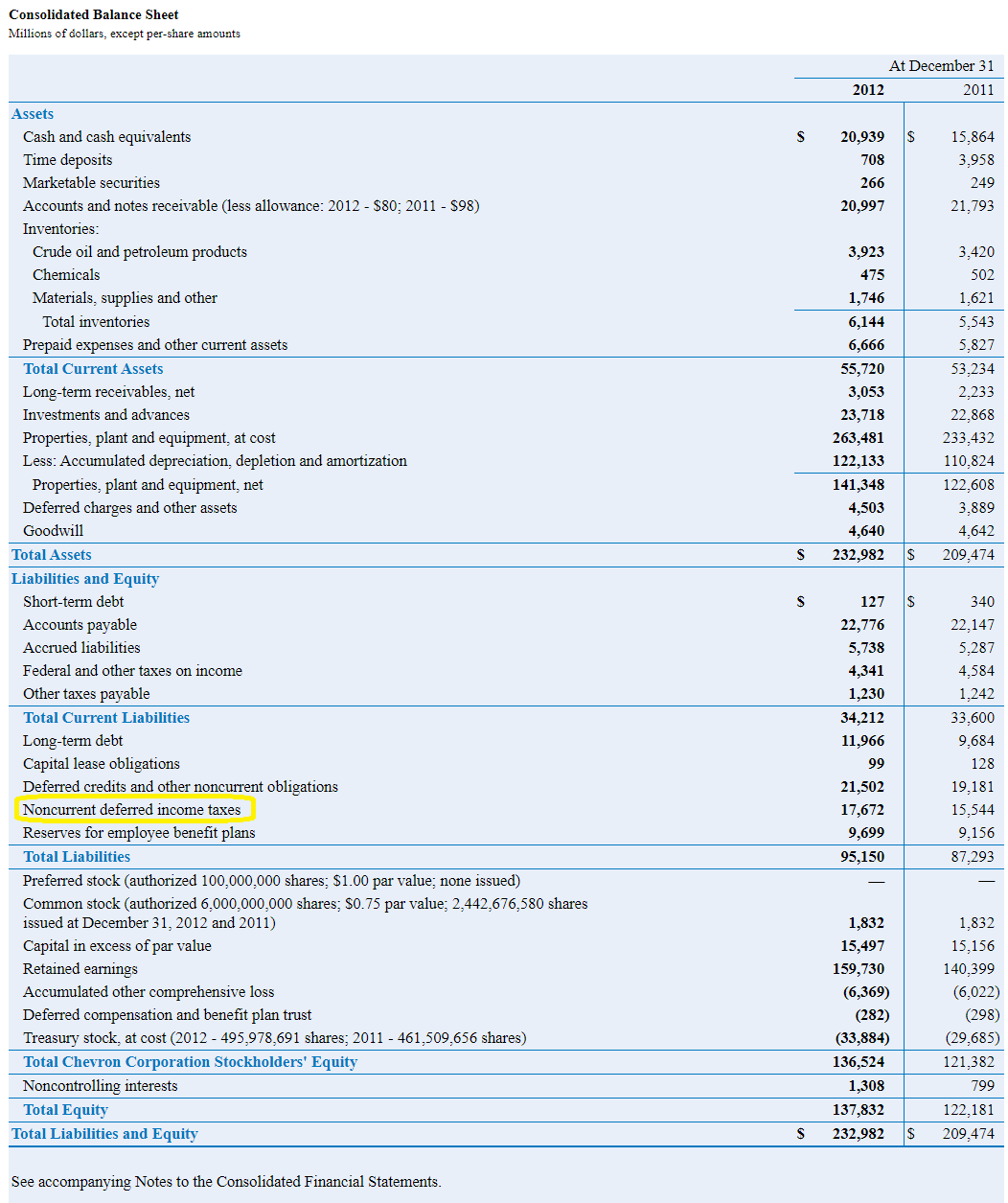
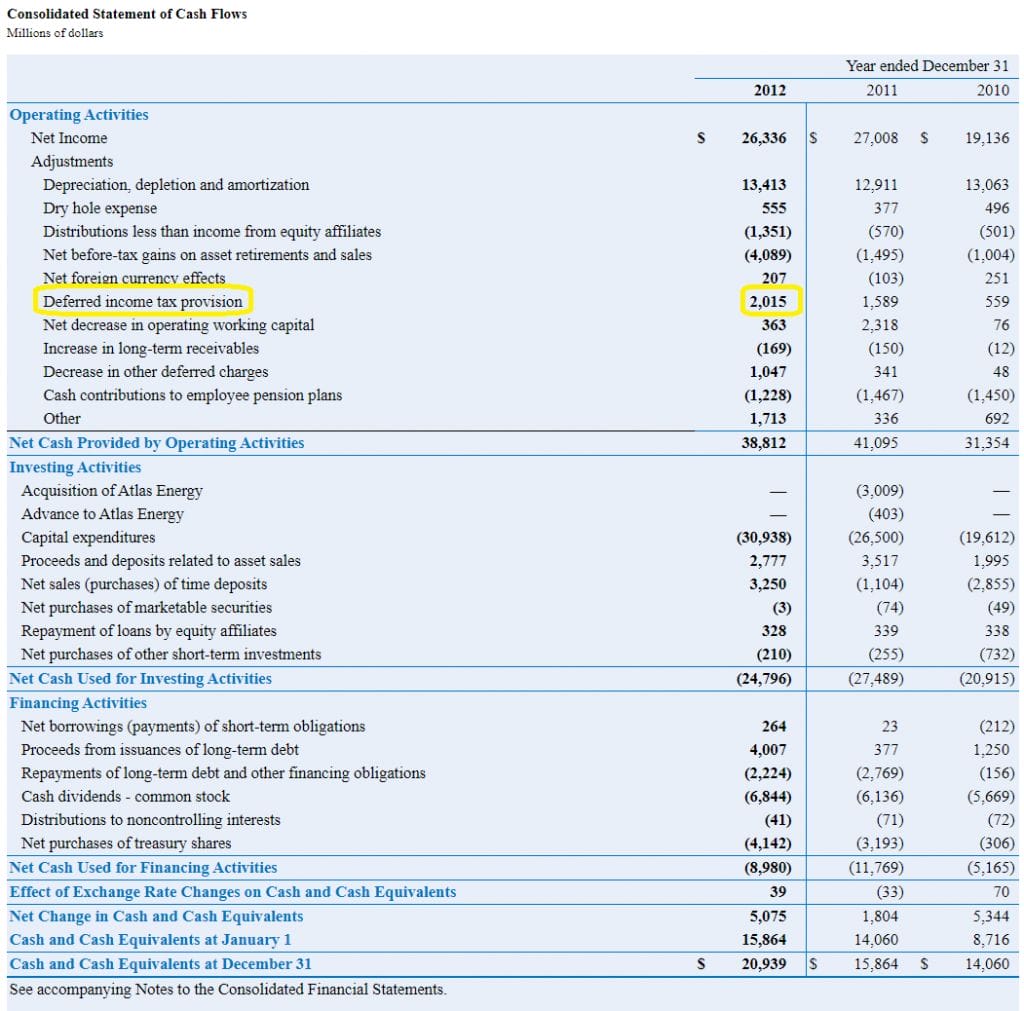
A deferred tax liability (dtl) is listed on the balance sheet that shows taxes that are payable in the future. Deferred tax liabilities is the liability that arises to the company due to the timing difference between the tax accrual and the date when the taxes are paid to the tax authorities, i.e., taxes get due in one accounting period but are not paid in that period. Ias 12 defines a deferred tax liability as being the amount of income tax payable in future periods in respect of taxable temporary differences.
The balance sheet liability approach with separate recognition of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities in ias 12 is based on financial accounting standard 109 accounting for income taxes (fas 109) its us gaap equivalent. (1) taxable temporary differences that will generate future tax (i.e., deferred tax liabilities) and (2) deductible temporary differences that will. What are the general circumstances on which deferred tax usually arise?
The definition of “deferred tax liability” is an account on a company's balance sheet that is a result of temporary differences between the company's accounting and tax carrying values, the anticipated and enacted income tax rate,. Adjust the deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability for any changes in tax laws or rates; Presentation on the balance sheet.
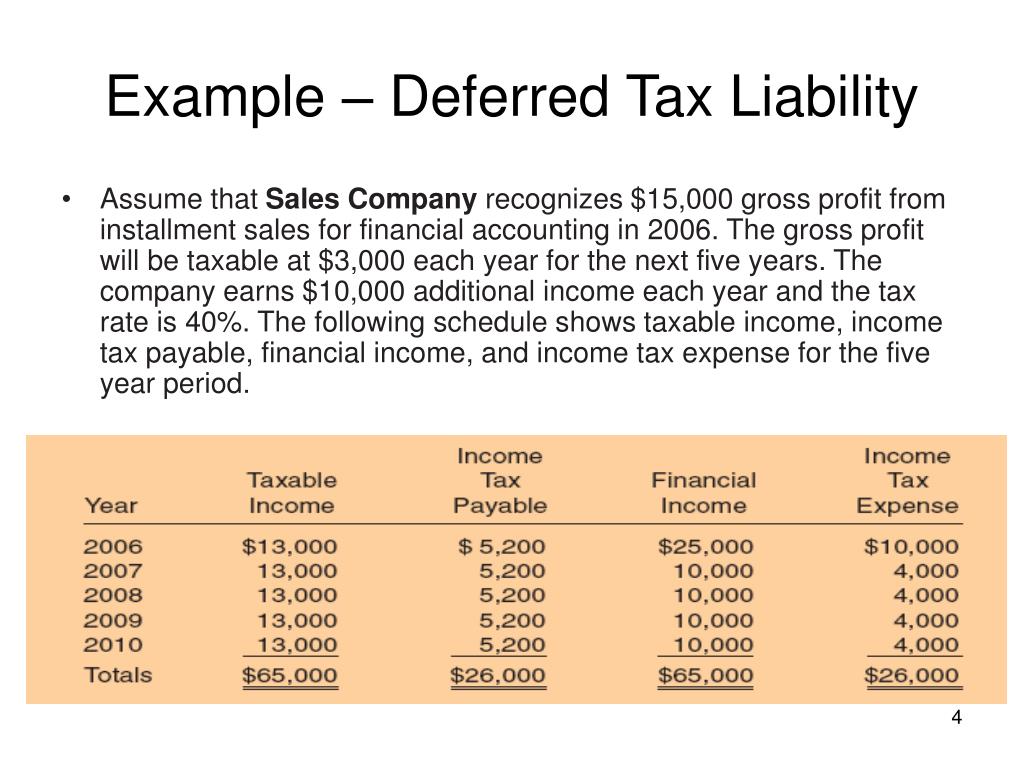
A deferred tax liability (dtl) or deferred tax asset (dta) is created when there are temporary differences between book (ifrs, gaap) tax and actual income tax. Here is a write up on all about dtl/dta, how it’s calculated and certain specific. A deferred tax asset is an item on the balance sheet that results from an overpayment or advance payment of taxes.
In the balance sheet, paragraph 29.23 of frs 102 requires that deferred tax liabilities are presented ‘within provisions for liabilities’ and deferred tax assets are presented ’within debtors’, unless the balance sheet formats have been adapted. There are two categories of temporary differences: Deferred tax assets and liabilities are the direct results of deferred taxes, which are based on temporary differences in recorded revenues or expenses between accounting books and tax returns.
Dtl/dta = temporary difference x tax rate; You can think of it as paying part of your taxes in advance (deferred tax asset) or paying additional taxes at a future date (deferred tax liability). Deferred tax is accounted for as per ias® 12, income taxes.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)