Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Tips About Deferred Tax Liability Balance Sheet

Deferred tax liability is a tax obligation recorded on a company's balance sheet that is not due for payment immediately.
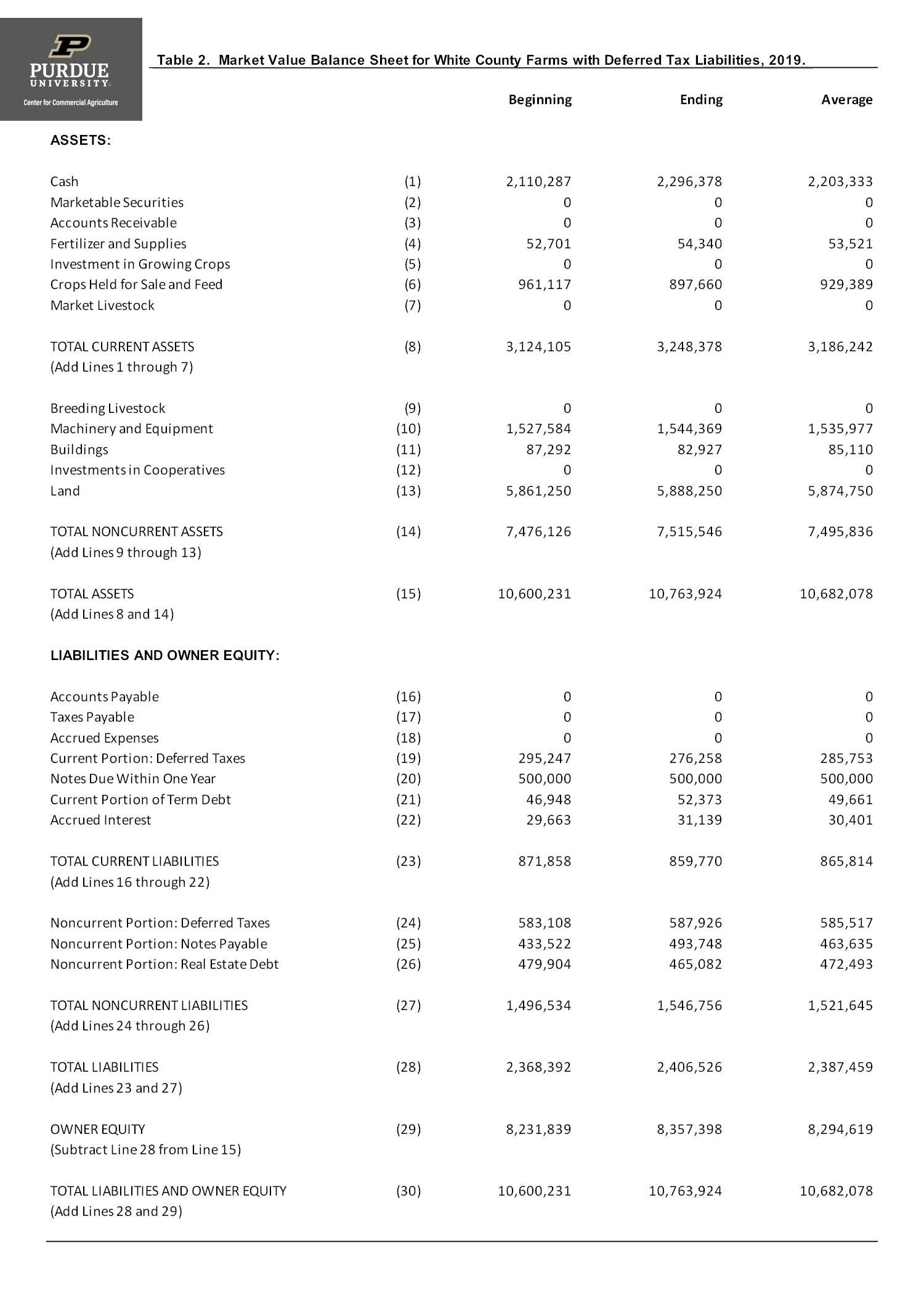
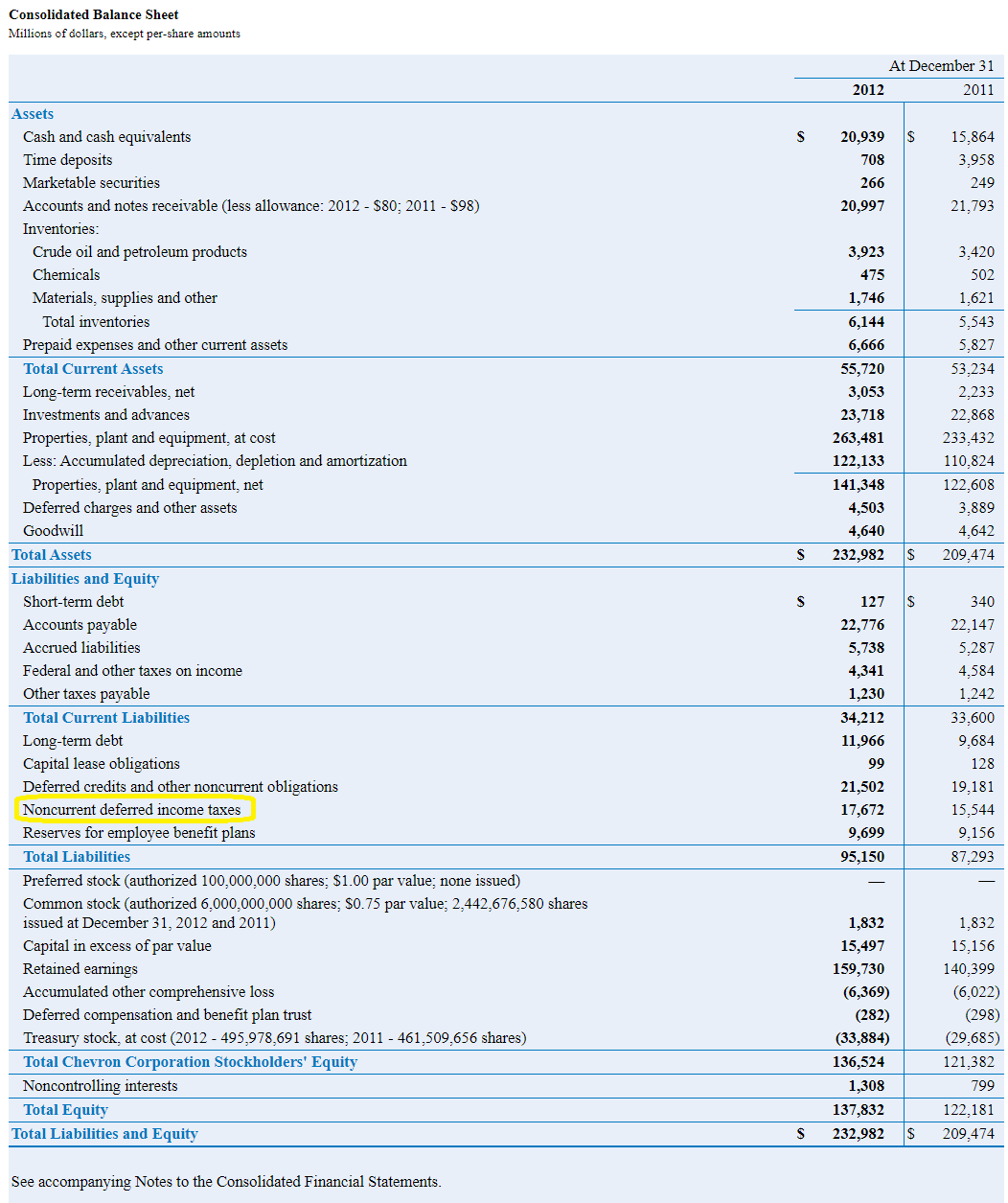
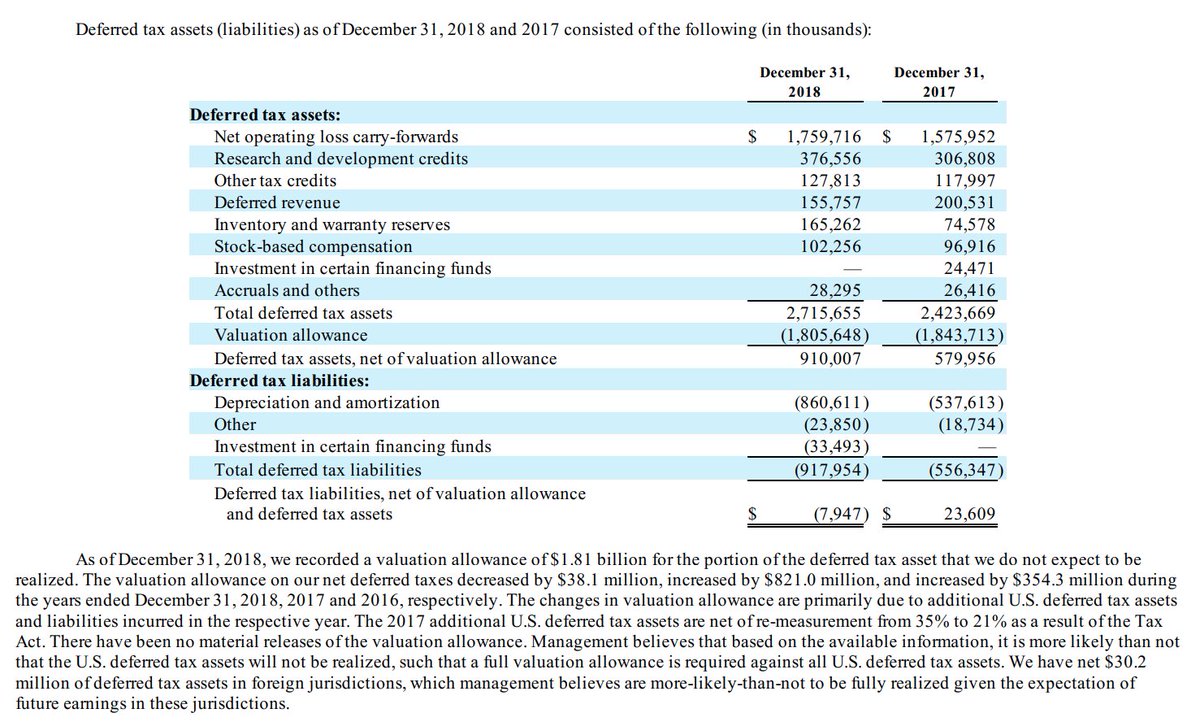
Deferred tax liability balance sheet. A deferred tax liability (dtl) is a tax payment that a company has listed on its balance sheet, but does not have to be paid until a future tax filing. A deferred tax asset represents a reduction in future tax liability and is reported on the balance sheet. Deferred tax liability (dtl) or deferred tax asset (dta) forms an important part of financial statements.
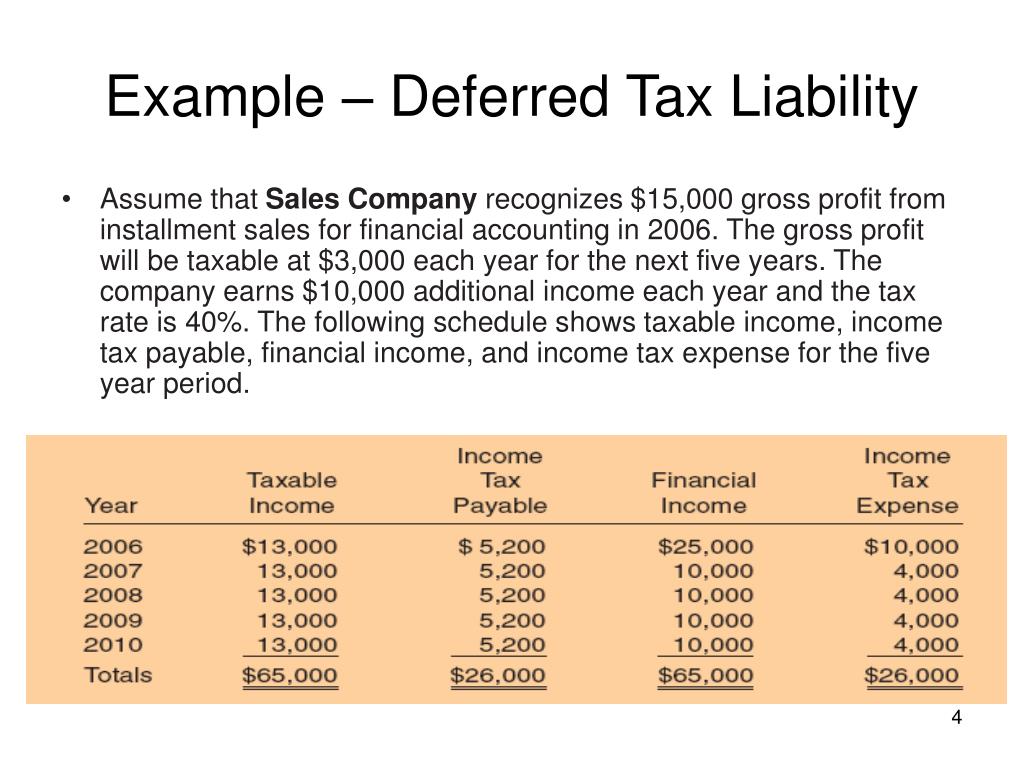
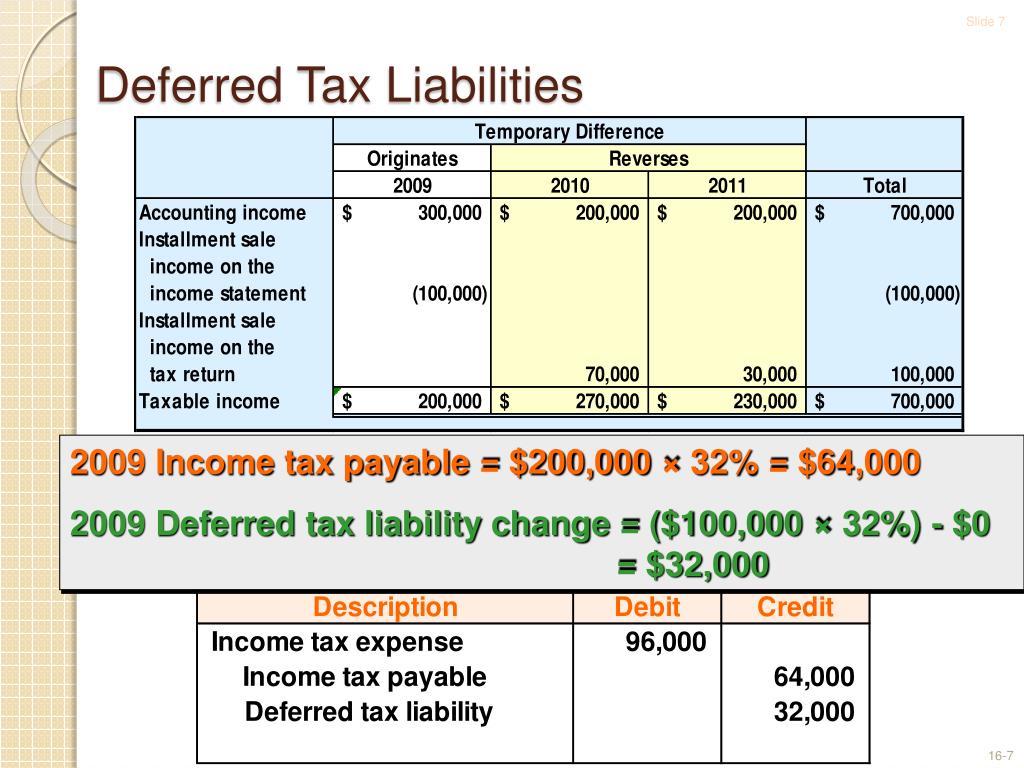
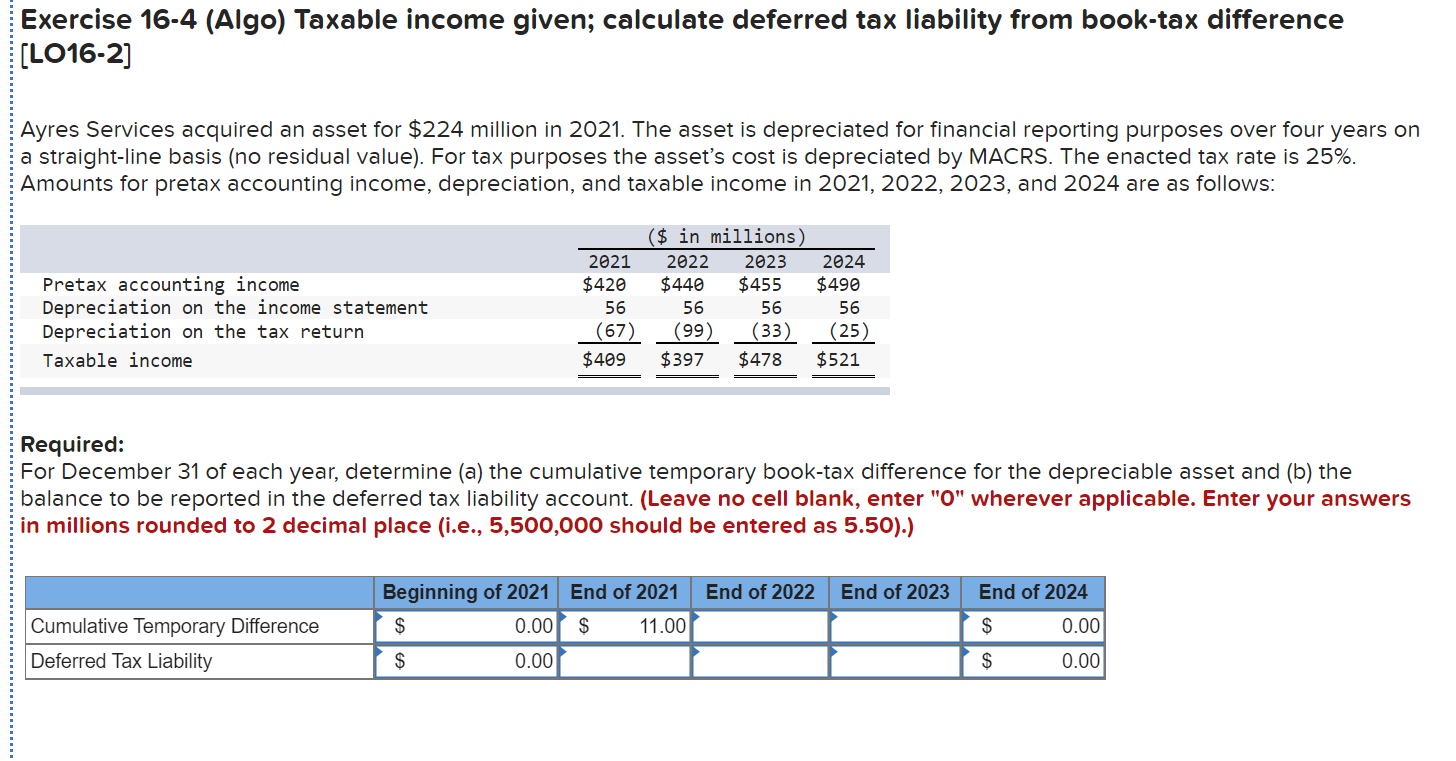
Deferred tax liability is calculated by finding the difference between the company's taxable income and its account earnings before taxes, then multiplying that. Deferred tax liabilities is the liability that arises to the company due to the timing difference between the tax accrual and the date when the taxes are paid to the tax. A deferred tax liability is a listing on a company's balance sheet that records taxes that are owed but are not due to be paid until a.
The difference of $300 will go to deferred tax liability on the company’s balance sheet. Firstly, we will be discussing items of assets side of balance sheet. There are two categories of temporary differences:
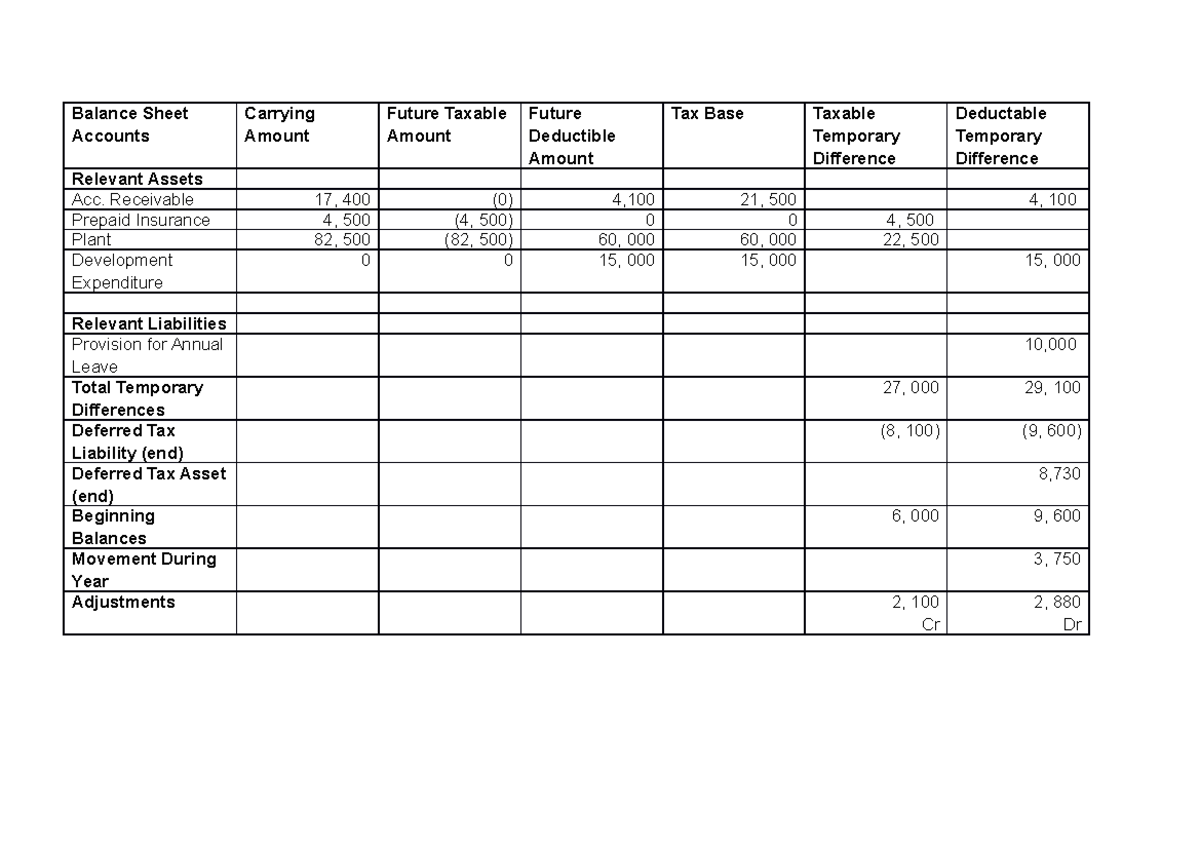
(1) taxable temporary differences that will generate future tax (i.e., deferred tax. Deferred tax asset in balance sheet. It arises from temporary differences.
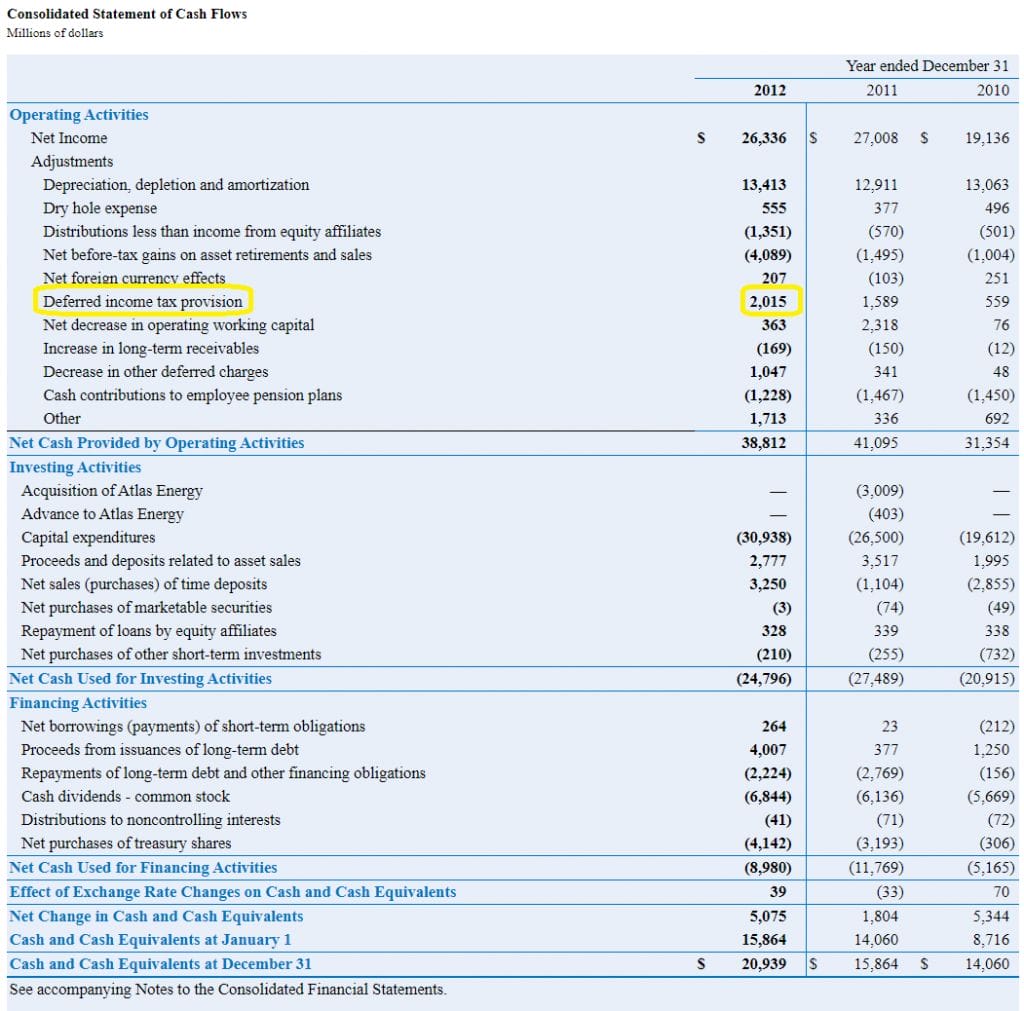
Changes to tax laws and regulations often impact the measurement of deferred tax liabilities on a company's balance sheet: The definition of “deferred tax liability” is an account on a company's balance sheet that is a result of temporary differences between the company's accounting and tax carrying. An amount of $1700 will be debited to current tax liability and credited to the cash account.
Tax rate changes affect the. Here positive results will mean creation of deferred tax liability and negative results will. Fundamentally, deferred tax balances represent the future tax impacts of recovering or otherwise consuming assets (e.g., by depreciating the asset) and settling liabilities (e.g.,.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Terms-d-deferred-revenue-Final-a8fb680c51014901a4b8f88ac7fb7f77.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)